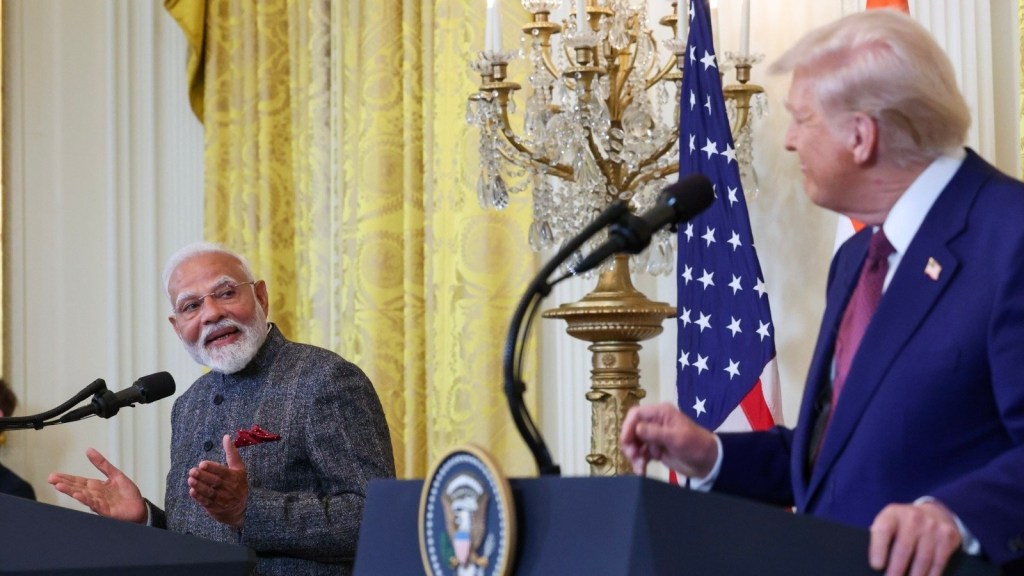
New Delhi/Washington — India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi is set to meet former U.S. President Donald Trump in the United States next month, signaling a renewed opportunity to address longstanding economic tensions and strategic cooperation between the two nations. While details of the agenda remain closely guarded, sources indicate the discussions will focus on trade, energy, regional security, and technology collaboration.
Historical Context: Evolving Relations
The India–U.S. relationship has long been shaped by periods of cautious engagement and strategic alignment. In the 1990s, economic liberalization in India and U.S. counterterrorism concerns formed the foundation for closer interaction. The 2008 U.S.–India Civil Nuclear Agreement marked a turning point, formalizing cooperation in energy, defense, and technology.
Under Modi, who assumed office in 2014, the bilateral partnership has deepened through joint military exercises, defense sales, and diplomatic coordination in the Indo-Pacific. Yet trade disputes have remained a recurrent challenge. Protectionist tariffs, regulatory concerns, and intellectual property debates have repeatedly tested the relationship, requiring delicate diplomacy to maintain strategic momentum.
Trade Frictions and Diplomatic Challenges
Earlier this year, the United States raised concerns over trade imbalances and India’s energy imports from Russia, prompting talks on potential tariff adjustments. India has offered selective reductions on American goods, including motorcycles, agricultural machinery, and spirits, contingent on reciprocal measures. Analysts note that these disputes reflect the broader challenge of balancing domestic economic priorities with international trade obligations, a recurring theme in India–U.S. relations.
Past incidents illustrate the complexities: the 2019 U.S. tariffs on steel and aluminum triggered Indian retaliatory measures, while intellectual property conflicts in pharmaceuticals and technology continue to influence negotiations. Strategically, disagreements over India’s defense procurement choices and engagement with Russia have added layers of complexity to an otherwise cooperative relationship.
The Modi–Trump Meeting: What to Expect
Scheduled to coincide with diplomatic engagements in Washington, the upcoming Modi–Trump meeting will likely be both symbolic and substantive. For Modi, the visit is an opportunity to reaffirm India’s role as a global economic and strategic actor, while addressing concerns over trade and technology collaboration. For Trump, the talks offer a platform to advocate for fair trade, strengthen political ties, and reaffirm U.S. influence in the Indo-Pacific.
Observers expect discussions to include energy security, cybersecurity, counterterrorism cooperation, and mechanisms for mitigating trade imbalances. While no formal agreements have been announced, the meeting is expected to send a signal about the durability of the India–U.S. partnership despite recurring frictions.
Balancing Past Lessons with Future Ambitions
The historical record suggests that bilateral tensions have often been managed through careful negotiation rather than confrontation. From tariff disputes to strategic misalignments, both nations have repeatedly demonstrated the ability to compartmentalize disagreements while advancing broader cooperation. Analysts caution, however, that domestic political pressures in both capitals may influence the scope and outcomes of discussions.
The meeting also comes at a critical moment in the Indo-Pacific region, where India seeks to assert its strategic autonomy while engaging with U.S.-led security frameworks. As both nations navigate evolving security challenges, from maritime security to regional stability, their dialogue will likely extend beyond bilateral trade and address broader geopolitical considerations.
Conclusion: Diplomacy in a Complex Era
The Modi–Trump encounter represents more than a bilateral discussion; it is a test of how two democratic powers manage the intersection of economics, security, and global influence. Historical disputes, strategic imperatives, and domestic considerations all converge, underscoring the intricate nature of contemporary diplomacy.
For India, the challenge is to balance economic protection with international obligations, while for the United States, the goal is to maintain strategic influence and fair trade practices. How the two leaders navigate these issues may define the trajectory of one of the world’s most consequential bilateral partnerships in the years to come.
1990s: Post-Cold War Engagement and Economic Liberalization
- 1991 – India undertakes major economic liberalization; U.S. recognizes opportunity for expanded trade and investment.
- 1993 – Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao visits Washington; bilateral discussions focus on trade, technology transfer, and nuclear nonproliferation.
- 1998 – India conducts nuclear tests in Pokhran; the U.S. imposes sanctions under the Glenn Amendment, halting military and high-tech exports.
- 1999 – U.S. sanctions begin to ease after dialogue on strategic stability; India–U.S. economic relations gradually normalize.
2000s: Nuclear Deal and Strategic Foundations
- 2000 – President Bill Clinton and Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee establish the U.S.–India Defense Policy Group to coordinate military and security collaboration.
- 2005 – President George W. Bush visits India; the leaders emphasize counterterrorism cooperation post-9/11.
- 2008 – U.S.–India Civil Nuclear Agreement signed; U.S. Congress passes legislation enabling civilian nuclear trade with India, formalizing a strategic partnership.
- 2009 – Prime Minister Manmohan Singh attends the UN General Assembly with President Barack Obama; discussions focus on climate, trade, and counterterrorism.
2010s: Expanding Strategic Cooperation and Trade Tensions
- 2014 – Narendra Modi becomes Prime Minister; emphasis on “Act East” policy and Indo-U.S. strategic partnership.
- 2015 – Modi attends the White House state dinner hosted by President Obama; talks cover trade, defense, and civil nuclear cooperation.
- 2017 – U.S. withdraws from the Paris Climate Agreement; India balances climate ambitions with U.S. relations.
- 2018 – Trade disputes emerge over steel and aluminum tariffs; India imposes retaliatory tariffs on 29 U.S. products.
- 2019 – Tariff tensions escalate; U.S. designates India as a “developing country” for trade negotiations; discussions include market access, intellectual property, and pharmaceuticals.
- 2019 – Modi meets Trump at the G20 summit in Osaka; strategic cooperation on Indo-Pacific security emphasized.
2020s: Strategic Convergence and Global Challenges
- 2020 – COVID-19 pandemic impacts trade; both nations coordinate on medical supply chains and vaccine production.
- 2021 – India participates in Quad summit (with U.S., Japan, and Australia) to address regional security, cybersecurity, and climate change.
- 2022 – Trade dialogue focuses on technology, semiconductors, and U.S. concerns about India’s trade barriers.
- 2023 – Modi and President Joe Biden meet in Washington; energy security, defense procurement, and climate cooperation are central topics.
- 2024 – Modi addresses U.S. Congress; discussions highlight Indo-Pacific security, counterterrorism, and fair trade measures.
- 2025 – Reports indicate Modi is scheduled to meet former President Donald Trump; expected agenda includes trade, regional security, technology collaboration, and Indo-Pacific strategy.
Recurring Themes and Observations
- Trade Tensions – Disputes over tariffs, market access, and intellectual property have consistently challenged bilateral relations, yet negotiations have generally prevented long-term breakdowns.
- Strategic Cooperation – Defense sales, joint military exercises, and Quad coordination demonstrate growing alignment on Indo-Pacific security and counterterrorism.
- Political Dynamics – U.S. administrations have alternated between engagement and pressure, while Indian governments have balanced domestic priorities with strategic partnerships.
- Global Context – Geopolitical shifts, from China’s rise to regional security crises, have amplified the strategic importance of the Indo-U.S. partnership.




Leave a comment